Command and Control MalOps
Command and control communication includes behaviors in which communication protocol or behavior deviates from expected communication behaviors in an attempt to communicate with an outside party for control of an environment. The MalOp types listed in this topic are triggered by various Command and Control behaviors.
These MalOps are part of the Verified group.
In this topic:
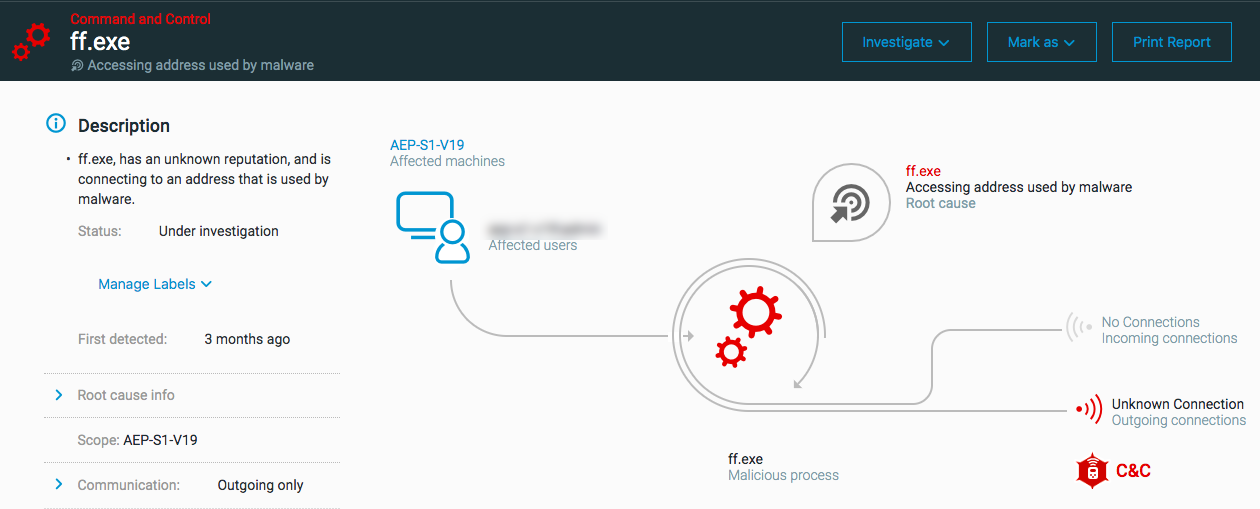
Accessing address used by malware
The MalOp for ‘Accessing address used by malware’ is triggered when a process connects to an address that is identified as being used by malware. Communication to addresses used by malware occurs when a connection opens or a DNS request is sent to an address known to be used by malware as part of the attacker’s attempt to use Command and Control.
Supported OS for this MalOp: Windows, Mac OS, and Linux
Examples of behavior that can trigger this MalOp:
Connections or DNS queries to locations used by malware
Next steps: Accessing address used by malware
Investigate each process that opened a connection to this specific address.
View the Element Details for the process and analyze them for other malicious indicators.
Investigate the connection as threat intelligence classifications change often, especially for malware domains.
Investigate the number of bytes transferred via the connection.
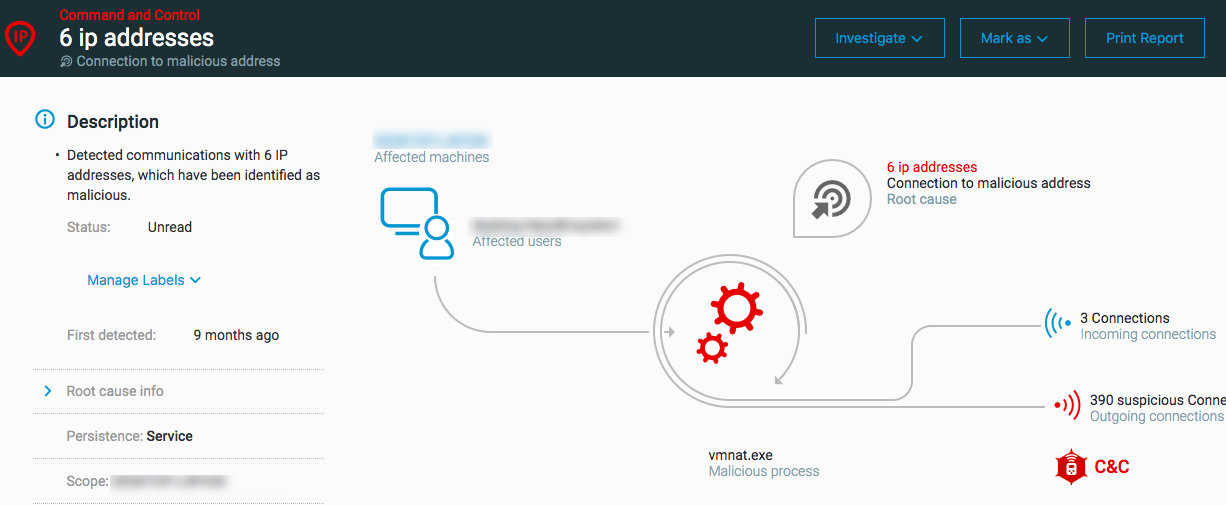
Connection to malicious address
The MalOp for ‘Connection to malicious address’ is triggered when a process opens a connection to an address classified as malicious by Cybereason Threat Intelligence. Communication to malicious addresses occurs when a connection opens or a DNS request is sent to an address identified as malicious by Cybereason threat intelligence as part of the attacker’s attempt to use Command and Control.
Supported OS for this MalOp: Windows, Mac OS, and Linux
Examples of behavior that can trigger this MalOp:
Accessing addresses classified as malicious by Cybereason Threat Intelligence
Use of an address classified as malware by Threat Intelligence
Next steps: Connection to malicious address
Investigate each process that opened a connection to this specific address.
View the Element Details for the process and analyze them for other malicious indicators.
Investigate the connection as threat intelligence classifications change often especially for malware domains.
Investigate the number of bytes transferred via the connection.
Connection to a malicious domain
The MalOp for ‘Connection to a malicious domain’ is triggered when a process creates a DNS query or a direct connection to a domain classified as malicious by Cybereason Threat Intelligence. Connections that use malicious domains are a sign of malicious communication, as like connections to malicious addresses, it is a behavior outside the norm for a connection.
Supported OS for this MalOp: Windows, MacOS X, and Linux
Next steps: Connection to malicious domain
Investigate each process that opened a connection to this specific address.
View the Element Details for the process and analyze them for other malicious indicators.
Investigate the connection as threat intelligence classifications change often especially for malware domains.
Investigate the number of bytes transferred via the connection.
Download from malicious domain
The ‘Download from Malicious domain’ MalOp is triggered when the Cybereason platform’s NGAV component detects a process downloading a payload from a malicious domain.
Supported OS for this MalOp: Windows
Next steps: Download from malicious domain
Investigate the process that opened a connection to the malicious domain.
Investigate the connection as threat intelligence classifications change often.
Remove the payload from the machine if necessary.
Malicious use of a Domain Generation Algorithm
The ‘Malicious use of a Domain Generation Algorithm’ MalOp is triggered when a process uses a Domain Generation Algorithm to communicate with a command and control server. The use of a Domain Generation Algorithm is an evasion technique as part of Command and Control communications. Domain generation algorithms are algorithms that, when applied to DNS lookups, will move through a series of Internet domains attempting DNS resolution until one is found that resolves to an IP address. This technique is designed to thwart firewall blocking by frequently changing the Internet domain name of the command and control server.
The Cybereason platform detects the use of a Domain Generation Algorithm by a process.
Supported OS for this MalOp: Windows, Mac OSX, and Linux
Next steps: Domain Generation Algorithm
Investigate the DNS requests made by looking at the related Suspicion and clicking the Suspicion detail line.
If there are multiple processes, investigate the processes with a DNS Query Unresolved from Domain Element -> Process Element investigation query.
Examine successfully resolved DNS queries where data was transferred (all types of DNS queries). To see the amount of transferred data, add the columns in the results for the amount of data transferred.
Malicious rclone.exe process masqueradied as another process to perform copy operations
The ‘Malicious rclone.exe process masqueraded as another process to perform copy operations’ MalOp is triggered when the rclone.exe process name is changed to another process name, and the renamed process then performs file copy operations.
Supported OS for this MalOp: Windows
Next steps: Malicious rclone.exe process masqueraded
Investigate the renamed process.
Kill the renamed rclone.exe process.
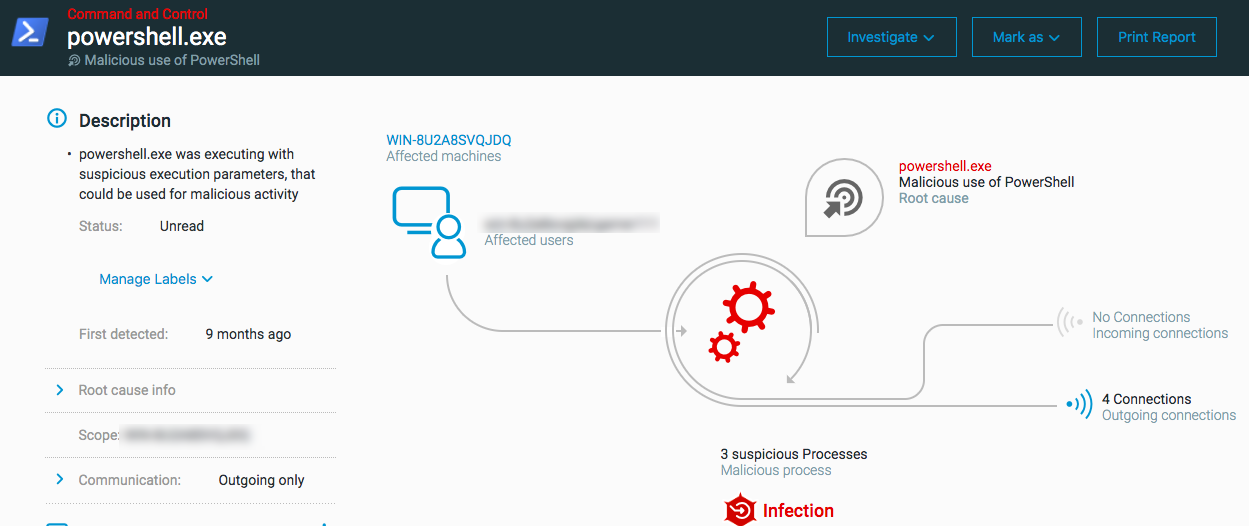
Malicious use of PowerShell
The MalOp for ‘Malicious use of PowerShell’ is triggered when the PowerShell program is used to download a script or run an obfuscated command. The malicious use of PowerShell involves a number of different misuses of PowerShell, including malicious downloads by a PowerShell program, malicious commands, and so forth.
Supported OS for this MalOp: Windows
Examples of behavior that can trigger this MalOp:
Detection by PowerShell protections
File downloads by PowerShell service
Malicious PowerShell payloads
Suspicious PowerShell parameters or command lines
Malicious PowerShell frameworks and commands, like Invoke or Empire
Obfuscated PowerShell commands or content
PowerShell execution by Microsoft Word
Next steps: Malicious use of PowerShell
Investigate the PowerShell command line and the decoded command line.
If there is PowerShell download activity, use the File Search to find and analyze the file downloaded.
Review connection activity associated with the PowerShell process and child processes.
Malicious use of NetSupport tool
The ‘Malicious use of NetSupport tool’ MalOp is triggered when an attacker performs malicious actions with the NetSupport remote access tool.
Supported OS for this MalOp: Windows
Next steps: Malicious use of NetSupport tool
Investigate the process hierarchy that includes the NetSupport tool.
Isolate the machine if needed.
Kill the NetSupport tool process if needed.
Malicious execution of PsExec process was launched by the ScreenConnect process
The ‘Malicious execution of PsExec process was launched by the ScreenConnect process’ MalOp is triggered when the ScreenConnect remote access tool is used to launch a malicious PsExec process.
Supported OS for this MalOp: Windows
Next steps: Malicious execution of PsExec process
Investigate the process hierarchy.
Isolate the machine if needed.
Kill the ScreenConnect and PsExec process (and other processes) if needed.
Malicious file in temporary folder run by ScreenConnect
The ‘Malicious file in temporary folder run by ScreenConnect’ MalOp is triggered when an attacker uses the ScreenConnect remote access tool to run malicious files in temporary folders on a machine.
Supported OS for this MalOp: Windows
Next steps: Malicious file in temporary folder
Investigate the process hierarchy.
Isolate the machine if needed.
Kill the ScreenConnect process.
Quarantine the nalicious files.
Process used Download and Execute
The ‘Process used Download and Execute’ MalOp is triggered when the Cybereason platform NGAV component detects the use of the PowerShell Download and Execute commands on a machine.
Supported OS for this MalOp: Windows
Next steps: Process used Download and Execute
Investigate the process that used the Download and Execute commands.
Investigate the connection as threat intelligence classifications change often.
Remove the payload from the machine if necessary.
ScreenConnect ran malicious unsigned file
The ‘ScreenConnect ran malicious unsigned file’ MalOp is triggered when an attacker uses the ScreenConnect remote access tool to run unsigned malicious files on a machine.
Supported OS for this MalOp: Windows
Next steps: ScreenConnect ran malicious unsigned file
Investigate the process hierarchy.
Kill the ScreenConnect process.
Isolate the machine if needed.
Quarantine the malicious files if needed.