MalOp Remediation Examples
The following examples demonstrate, step-by-step, how to choose and execute remediation options for different MalOps.
In this topic:
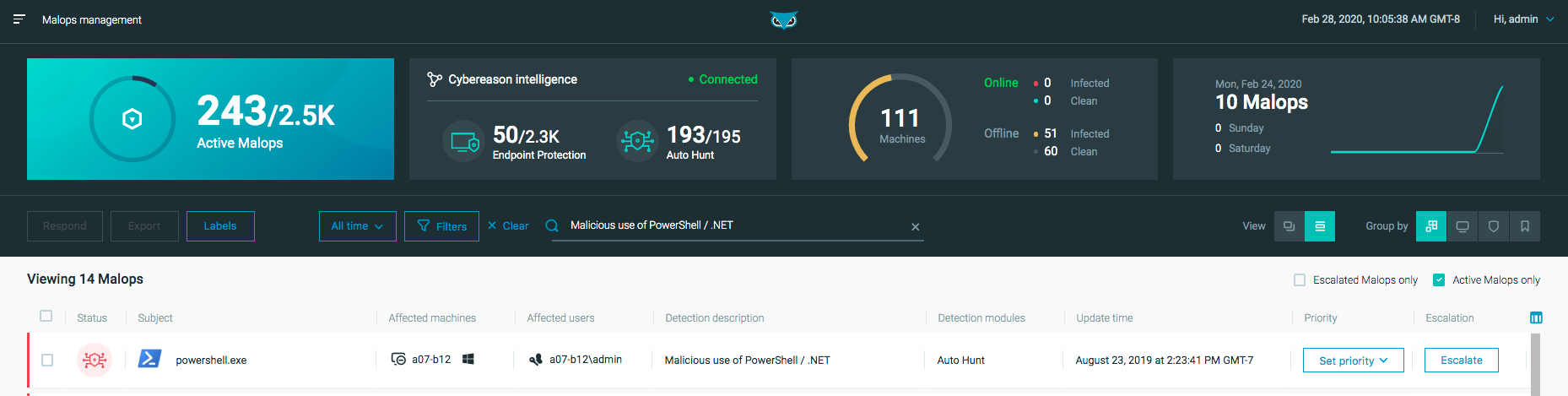
Example 1: Respond to the Malicious use of PowerShell MalOp
For the first example, you will look at a MalOp associated with PowerShell use.
PowerShell is a legitimate tool that can also be used by attackers for actions such as privilege escalation and code injection.
In this example, the PowerShell MalOp has the Command and Control detection type because the powershell.exe process tried to execute using parameters that could indicate command and control activity.
Let’s look at the MalOp’s behavior from the Malop details screen. In the following image, the Malop details screen shows the following behavior:
In the MalOp Overview, the Cybereason platform lists the following characteristics for the MalOp:
1 user
1 machine
3 suspicious processes in total
2 outgoing connections
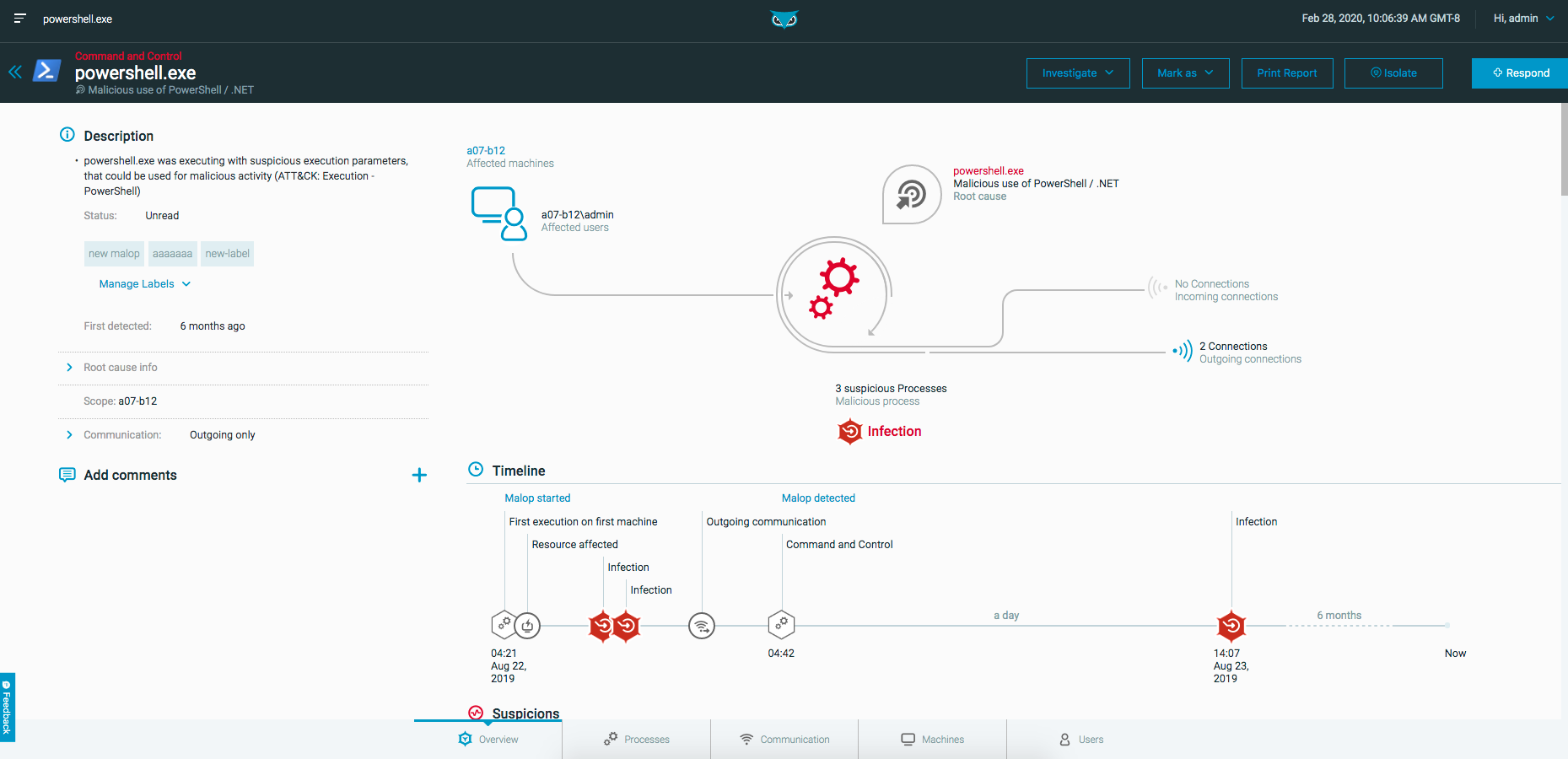
The Timeline shows repeated infection, persistence, and communication with a Command and Control (C&C) server. This behavior is typical in the attack lifecycle.
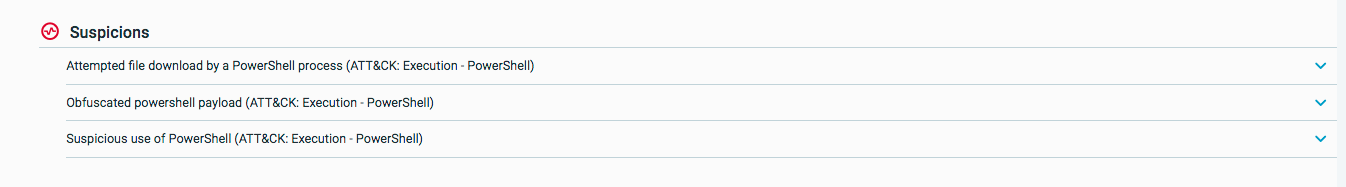
Below the Timeline are several suspicions, indicating an advanced attack. Suspicions include:
Attempted file download by a PowerShell process
Obfuscated PowerShell payload
Suspicious use of PowerShell
You can access the Investigation screen for related process directly from the Processes tab to view more details about the suspicious processes. You can even view the PowerShell commands themselves, in the Element details pane’s Properties section. In this example, you can see a download command and an encoded command.
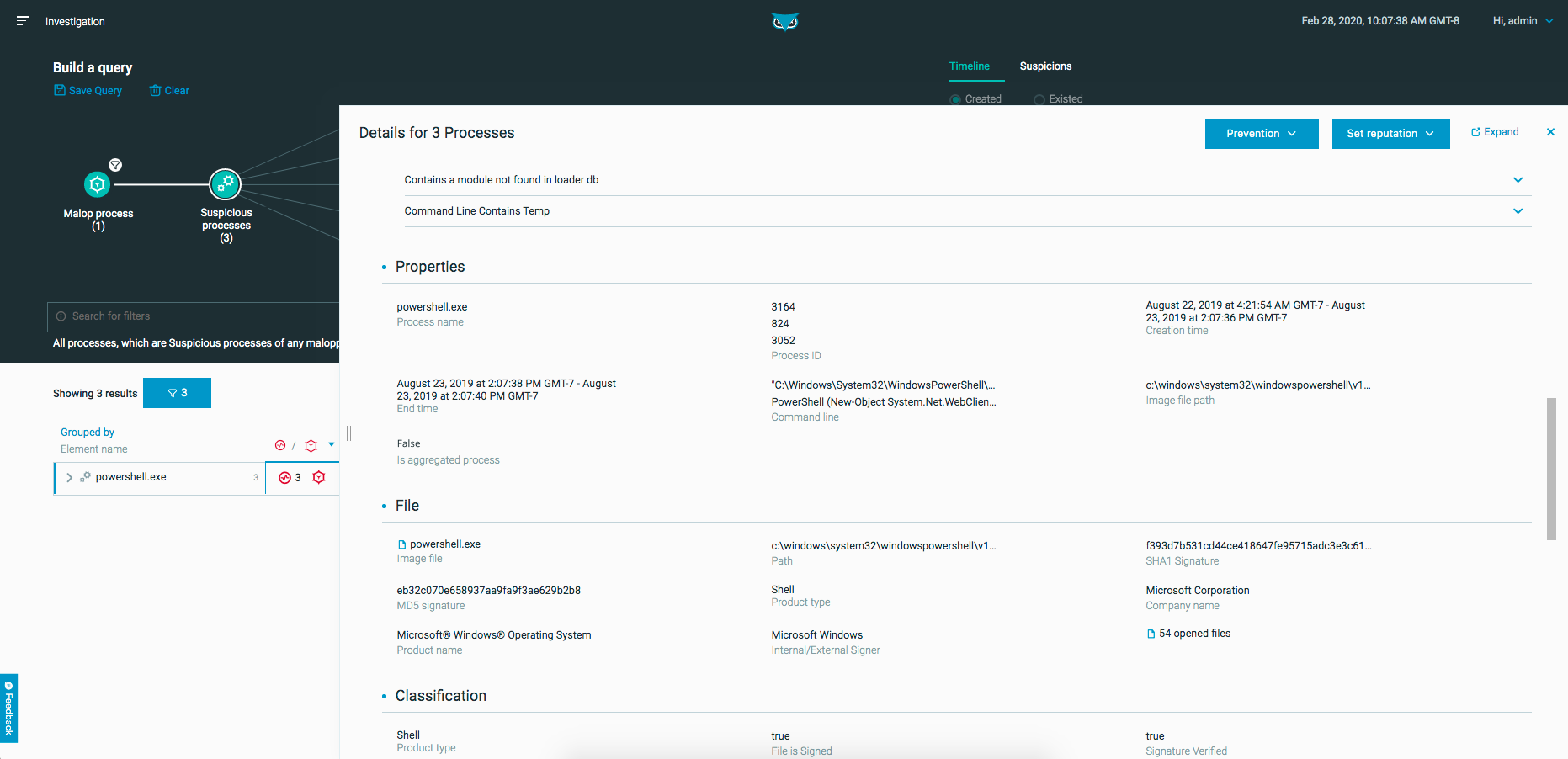
Your conclusion is that PowerShell is downloading a payload from a malicious domain, and that payload is running on the machine that the Overview section lists. This is a serious attack which requires an immediate response.
As shown in Example 1 above, you can respond with remediation and prevention from the Malop details screen. Use the available response options to stop items associated with the attack, such as isolating the machine.
After your initial response, you should conduct a deeper investigation to determine if any other machines have been exposed to this attack. To learn more about investigation, see Perform a Hunt or Investigation.
Example 2: Respond to Behavioral Ransomware
In most cases, the Cybereason platform lets you decide first how to respond to a Malop. An exception is behavioral ransomware. In this case, attackers can encrypt a user’s files, causing damage very quickly. You can configure Cybereason sensors to take immediate action and suspend behavioral ransomware before the ransomware can cause damage. See Set the Canary File-Based Anti-Ransomware Modes for more information.
Note
Behavioral Ransomware detection is available for machines running the Windows operating system.
Here is an example of behavioral ransomware:
In this case, the Cybereason platform already suspended the ransomware and saved the user’s files from being encrypted.
You can select Respond > Prevention to prevent the ransomware’s execution on other machines where Application Control is enabled.
At this stage, you should conduct a deeper investigation to determine if any other machines have been exposed to this attack. To learn more about investigation, see Perform a Hunt or Investigation.


